How Monopoly Affects Wealth Distribution
Monopolies significantly influence wealth distribution within an economy. When a single entity dominates a market, it can set prices and control supply, often leading to higher profits for the monopolist and less competitive pricing for consumers. This concentration of market power can result in wealth accumulating with the monopolist, exacerbating income inequality. In this blog, we will explore the various ways monopolies impact wealth distribution, examining both the economic mechanisms at play and their broader societal implications.
Is Monopoly Affects Wealth Distribution
Monopoly inequality in microeconomics looks at how monopolies affect income differences. Monopolists have significant market power, allowing them to set high prices and limit supply, leading to substantial profits. This concentration of wealth among a few individuals creates large income gaps. Additionally, monopolies stifle competition and innovation, limiting opportunities for small businesses and workers, and further widening the gap between the rich and everyone else.
Understanding Monopoly and Market Power
A monopoly occurs when a single company controls the market for a specific product or service. This control allows the company to set prices and limit supply, creating barriers for competitors. Monopolies gain power through early advantages, which can negatively impact competition and consumer interests. Understanding monopolies and their effects is crucial for developing strategies that promote competition and efficiency in markets.
Example: De Beers historically dominated the global diamond market.
While some market power is common in many industries, excessive power can be harmful.
- Higher Prices: Monopolists often set higher prices than in competitive markets, reducing consumer benefits and transferring wealth from consumers to producers.
- Supply Restrictions: By limiting supply, monopolies create scarcity, leading to unmet demand and economic inefficiencies.
- Barriers to Entry: Dominant firms use tactics to prevent new competitors from entering the market, reinforcing their dominance.
These issues highlight the need for regulations to curb monopolistic practices, ensuring healthy competition and benefiting consumers and society.
How Monopolies Contribute to Wealth Inequality
Unchecked monopoly power has more than just economic costs; it can also have significant social impacts, particularly by increasing wealth inequality:
- Profit Concentration: Monopolies can control prices and earn high profits due to their market dominance. However, these profits often lead to unequal wealth distribution, increasing inequality.
- Wage Suppression: With few competitors, monopolistic firms can keep wages low. This widens the income gap between workers and business owners.
- Political Influence: Large businesses can influence regulations and policies in their favour due to their wealth. This power helps them maintain dominance and block new competitors.
- Reduced Innovation: While some argue that monopolies invest in innovation, others believe that lack of competition hinders innovation. This slows economic development and disproportionately affects those at the lower end of the economic scale.
Understanding Monopolies and Income Inequality
Monopolies are market structures where a single entity or a small group controls the supply of a specific product or service. This control over the market can lead to significant income inequality within a population. Income inequality refers to the uneven distribution of earnings among individuals or households within a country.
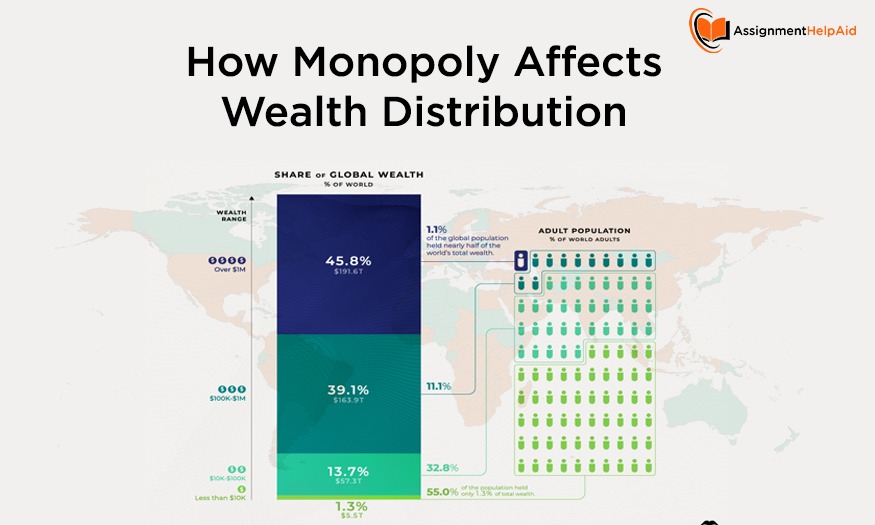
When monopolies gain dominance in a market, they can exploit their power to capture economic rents, which are essentially excess profits. These profits often benefit the business owners and shareholders, further concentrating wealth among a select few. For example, tech giants like Amazon, Google, and Facebook have faced scrutiny for their monopolistic tendencies. They have been accused of manipulating market dynamics to their advantage, raising concerns about consumer choice, privacy, and economic fairness. This ability to control markets and generate substantial profits can exacerbate existing income disparities, pushing those at the top of the economic ladder even higher.
Policy Responses to Monopolies
To address the negative impacts of monopolies on income inequality and market competition, governments can implement various policy measures. One common approach is the use of antitrust laws, which are designed to prevent monopolistic behavior and promote fair competition. These laws aim to ensure that monopolies do not engage in anti-competitive practices that harm consumers or hinder market entry for competitors.
For instance, in the 1980s, the U.S. government initiated the deregulation and breakup of AT&T, a telecommunications monopoly. This process, known as divestiture, aimed to reduce AT&T’s control over the telephone service market and create opportunities for other players to enter the telecommunications industry. By breaking up monopolies and fostering competition, policymakers seek to level the playing field and promote economic opportunity for all.
Student Tips: Understanding Monopoly Power
When studying monopolies, it’s important to look at how they form, how they stay in power, and what impact they have on competition. Understanding how monopolies arise, whether through technology, control of resources, or legal rights like patents, helps grasp why they last. Examining the barriers they create for competitors, like high start-up costs or exclusive contracts, sheds light on their staying power.
Graphical analysis is a handy tool for understanding the effects of monopolies. By studying demand and marginal costs, students can see how monopolies restrict output and raise prices, leading to less benefit for consumers and producers. Comparing these outcomes to competitive markets shows the inefficiencies caused by monopoly power. This insight highlights the importance of promoting competition and controlling negative economic effects.
Final Thoughts
In summary, understanding how monopolies influence wealth distribution is crucial in economics. Monopolies wield significant power, leading to high profits and wealth concentration among a few. This exacerbates income inequality and stifles competition and innovation. Effective regulation, such as antitrust laws, is necessary to promote fair competition and economic opportunity for all. For students, grasping how monopolies form and affect markets is essential, with graphical analysis aiding in visualizing their impact. This understanding lays the groundwork for addressing economic inequities and fostering a more balanced economic system.
Microeconomics Assignment Help for understanding Monopoly
Are they struggling with understanding monopoly and inequality concepts in microeconomics? Many students find these topics tricky and make mistakes in their assignments. Our microeconomics assignment helps service offers:
- Expert Guidance: Our team of certified microeconomics tutors provides clear explanations of concepts, descriptions of models, and methods to solve assignments.
- Customized Support: We tailor our assignment solutions to meet your specific requirements and follow your assignment guidelines, whether you need help with a numerical problem or an entire project.
- 24/7 Availability: Need help with your papers at any time? Just reach out to us! We’re here round the clock to help you meet your deadlines and succeed in your studies.
Contact us now to get assistance from our qualified experts and master microeconomic concepts. Our microeconomics homework help services cover everything from creating graphs to analyzing problems. Get guidance on tackling even the toughest questions in microeconomics.

